Lake Tahoe Clarity Report: Trend Stable, Not Improving
Annual Report Suggests Deep Dive into Particle Science

By Kat Kerlin, June 16, 2025
Lake Tahoe, Calif./Nev. - Lake Tahoe’s long-term clarity record is not trending worse, nor is it improving, according to the 2024 annual clarity report from the University of California, Davis’ Tahoe Environmental Research Center (TERC).
The report, released today, documents steep declines in clarity through the 1990s before leveling off in recent years. In 2024, annual average clarity for Lake Tahoe was 62.3 feet. That is down from last year’s average of 68.2 feet, but it is not statistically worse, the report notes. The number is a measure of the depth at which a white disk remains visible underwater.
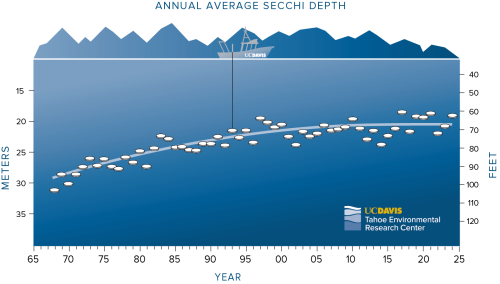
“We should embrace the improvements we have seen since the 1990s,” said Stephanie Hampton, director of TERC and a UC Davis professor in the Department of Environmental Science and Policy. “It’s not, at this point, noticeably worse. But it’s not getting better, and we need to find out why.”
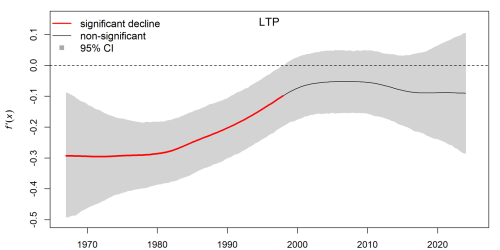
Seasons of change
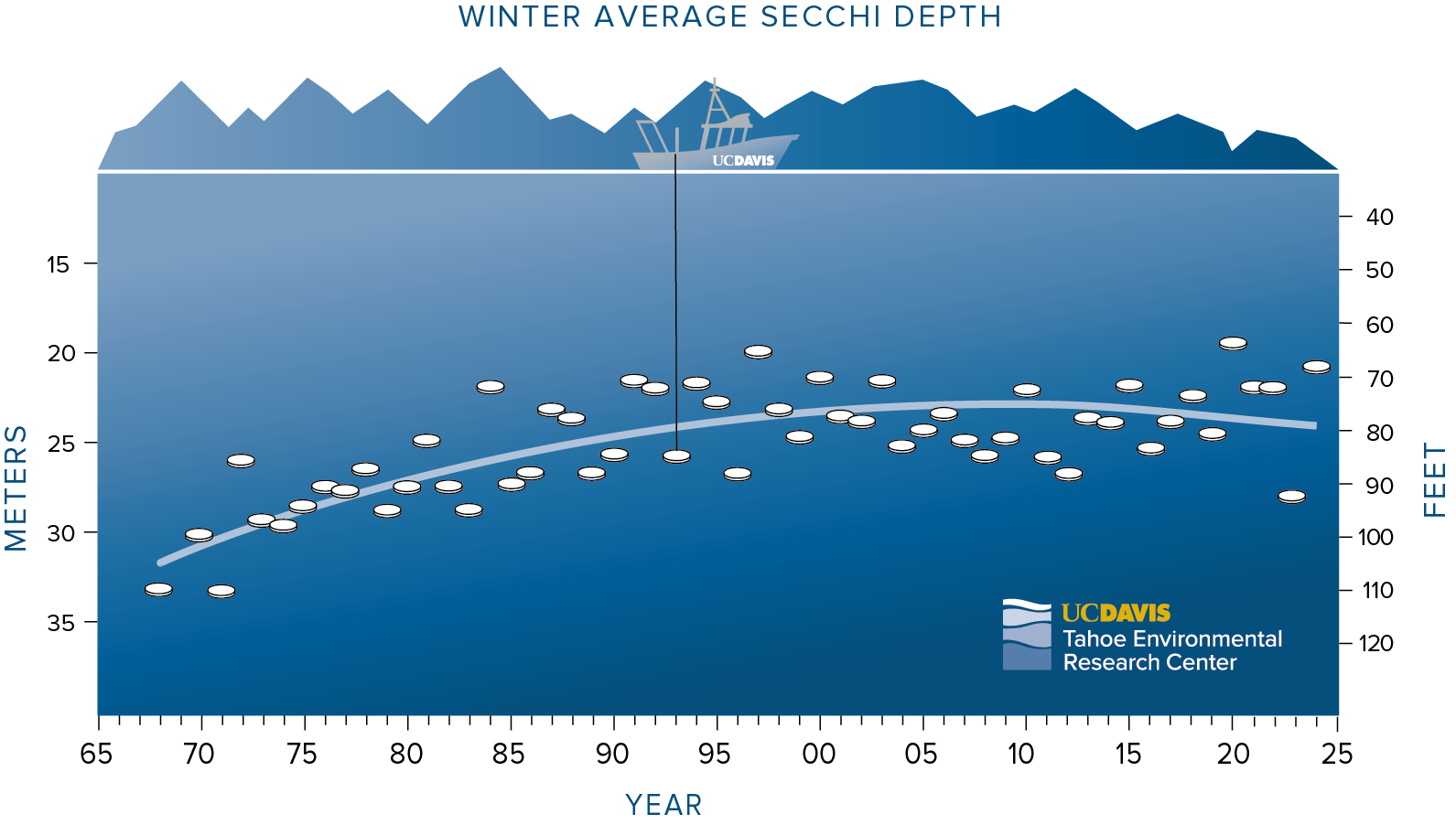
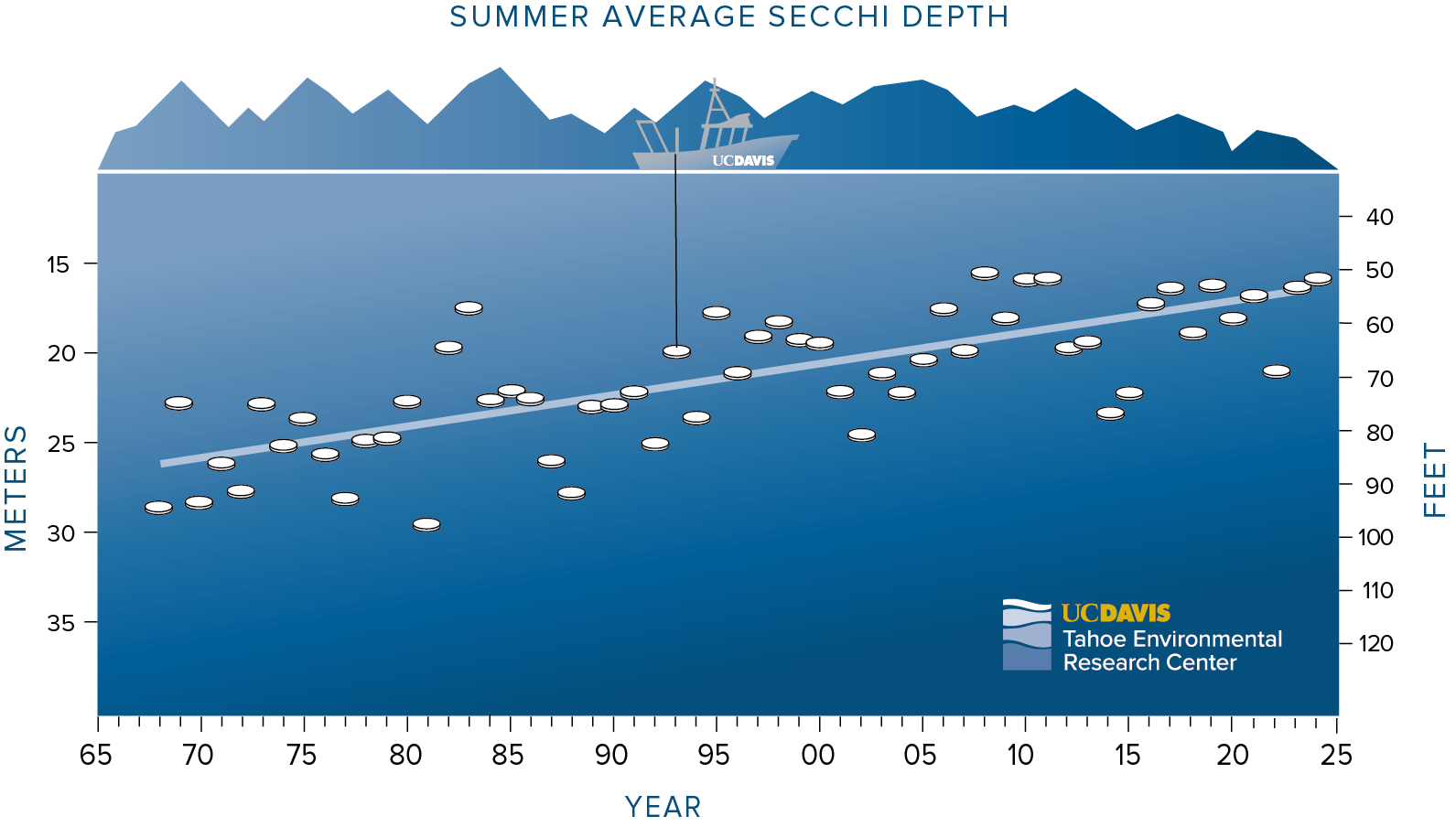
Winter clarity has been stable or improving in recent years, though was relatively poor (68.9 feet) in 2024 following an exceptional 91.9-foot average the winter prior. The past 10 summers have marked some of the worst averages on record, with 2024 summer averages measuring just 53.4 feet below the surface.
Detailed investigations conducted about 20 years ago pointed to sediment as the primary particles driving Tahoe’s clarity. A variety of management actions to reduce sediment runoff into the lake followed. Today, Lake Tahoe faces new challenges. It is warmer, more affected by wildfire and smoke than it was in recent decades, and its ecology is being impacted by aquatic invasive species.
“It may be the lake is different than it was 20 years ago, when these policies and practices were implemented,” said Hampton, a freshwater ecologist who joined TERC as its new director this past fall. “We need to investigate these particles again to find out what kind of particles they are. Are they still mostly sediment? Or are there more algae, wildfire ash or other particles? That may be key to understanding why water clarity is not improving.”
The report said future research should use new data, tools and technologies to reexamine the nature of clarity-reducing particles. This will help reveal the extent to which biology — such as algae — and physical processes influence water clarity at Lake Tahoe.
Under the Lake Tahoe Environmental Improvement Program, or EIP, the states of California and Nevada, along with more than 80 public and private organizations, are actively working to restore lake clarity to its historic 97.4 feet. Projects to treat stormwater and restore wetlands are so far capturing more than 500,000 pounds of fine sediment particles every year.
“Science-driven policies have underpinned Lake Tahoe’s protection for decades, and seeing lake clarity stabilize is an indicator that we are making progress,” said Julie Regan, executive director of the Tahoe Regional Planning Agency, which leads the EIP. “However, the lack of improvement is concerning, and we will continue to work closely with the science community to understand where to direct our management efforts next.”
Historical Depth
Clarity is measured as the depth to which a 10-inch white disk, called a Secchi disk, remains visible when lowered into the water. In 2024, UC Davis scientists took 27 readings at Lake Tahoe’s long-term index station and 12 readings from the mid-lake index station. View the historical clarity readings from 1968-2024.
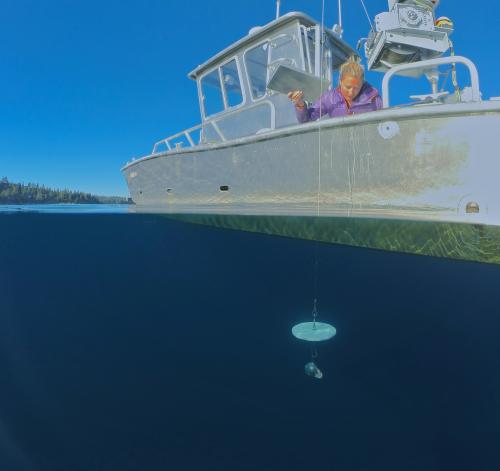

UC Davis has been measuring clarity and other health indicators at Lake Tahoe since 1968. Clarity is just one measure of the health of the watershed, but TERC’s measurements of clarity loss in the 1950s and 1960s became central to efforts to protect the watershed from pollution and unplanned development.
UC Davis works with the Tahoe Science Advisory Council and partners across the Tahoe Basin to help inform policymakers and the community on strategies to protect the lake and stabilize the decline in clarity that occurred following the mid-20th century development boom.
Partly in response to TERC’s early findings on Lake Tahoe’s clarity loss, the states of Nevada and California created the Tahoe Regional Planning Agency in 1969 to lead the collaborative effort to protect and restore Lake Tahoe. The agency continues to look to researchers to help prioritize restoration projects. Over several decades, EIP partners have improved or decommissioned more than 800 miles of roadways and restored or enhanced over 1,450 acres of damaged wetlands to stop fine sediment and other pollutants from entering the lake.
Media Resources
- Stephanie Hampton, UC Davis Tahoe Environmental Research Center, sehampton@ucdavis.edu
- Kat Kerlin, UC Davis News and Media Relations, 530-750-9195, kekerlin@ucdavis.edu
- Jeff Cowen, Tahoe Regional Planning Agency, 775-589-5278, jcowen@trpa.gov
Read the full 2024 Lake Tahoe Clarity Technical Summary.
Press kit of images and figures. For download with credit (in file).
